

Dr. Linda Li, Professor Harold Robinson/Arthritis Society Chair, Canada Research Chair, UBC & Arthritis Research Centre.
We developed a web application called FitViz. It allows physiotherapists and patients to use the physical activity data collected from Fitbit fitness trackers during consultations.
Next, we conducted a four-week study with 20 patients (inflammatory and knee osteo-arthritis arthritis) and 7 physiotherapists to evaluate the feasibility of FitViz, and understand the experiences of the physiotherapists and the patients.
We used semi-structured interviews to understand how physiotherapists used FitViz, and if and how it changed the nature of their consultation.
“Oh, I didn’t do a good job: How objective data affects physiotherapist-patient conversations for arthritis patients.”
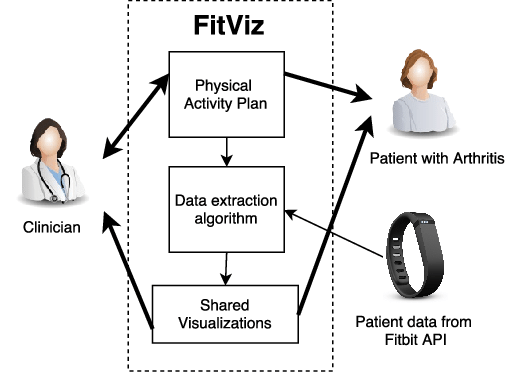
We found that the use of objective data allowed the physiotherapist-patient conversations to be patient-driven, and allowed goals to be realistic and data-driven. However, the use of objective data also caused some patients to feel guilty, which has implications on the use of pervasive healthcare technology in clinical settings.
After iterative improvements, we initiated a larger, longitudinal study.
References:
Ankit Gupta, Tim Heng, Chris Shaw, Diane Gromala, Jenny Leese and Linda Li. 2020.
“Oh, I didn’t do a good job: How objective data affects physiotherapist-patient conversations for arthritis patients.”
Proceedings of the 14th EAI International Conference on Pervasive Computing Technologies for Healthcare.
Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 156–165. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3421937.3421991
Li LC., Feehan LM., Xie H., Lu N., Shaw C., Gromala D., Aviña-Zubieta JA., Koehn C., Hoens AM., English K., Tam J., Therrien S., Townsend AF., Noonan G., Backman CL. (2020). “Efficacy of a Physical Activity Counseling Program With Use of a Wearable Tracker in People With Inflammatory Arthritis: A Randomized Controlled Trial.”Arthritis Care & Research (Hoboken).
2020 Dec;72(12):1755-1765. DOI: 10.1002/acr.24199. PMID: 32248626 Clinical Trial.
